I/O Streams in Java (Input/Output stream) .
Input/Output Stream
Java IO (Input and Output) is a process of reading data from a source and writing text data to a destination(file).
Stream :
Stream in Java represents sequential flow (or unbroken flow) of data from one place to another place.
- Java uses the concept of a stream to make I/O operations fast.
- The java.io package contains all the classes required for input and output operations. We can perform file handling in Java by Java I/O API.
1.Input stream
2.Output stream
1.Input stream :
- An InputStream is used to read data from a source, such as a file, network socket, or an array.
- It is an abstract class.
- Some inbuild subclasses for read data as from source follow
- FileInputStream : for reading data from a file .
- ByteArrayInputStream : for reading data from a byte array.
- SocketInputStream : for reading data from a network socket.
2.Output Stream:
- An OutputStream is used to write data to a destination, such as a file, network socket, or an array.
- It is also an abstract class, and you use its subclasses to handle specific data destinations.
- Some commonly used subclasses for write data to destination as follow
- FileOutputStream : for writing data to a file ,
- ByteArrayOutputStream : for writing data to a byte array
- SocketOutputStream : for writing data to a network socket.
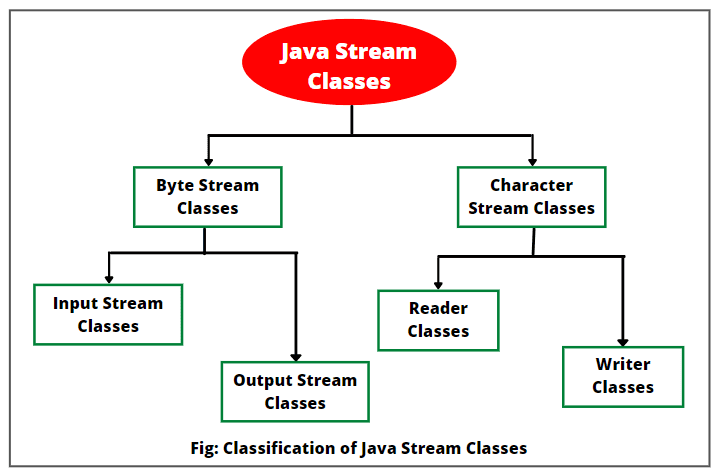
Stream Classes in Java
Java's I/O streams are categorized into two types:
1.byte streams class (support for handling I/O operations based on bytes)
2.character streams class (support for managing I/O operations on characters)
1.Byte streams class
- Byte streams in Java are designed to provide a convenient way for handling the input and output of bytes (i.e., units of 8-bits data).
- We use them for reading or writing to binary data I/O.
- Byte streams are especially used when we are working with binary files(Only Machine readable) file such as executable files, image files, and files in low-level file formats such as .zip, .class, .obj, and .exe.
There are two kinds of byte stream classes in Java. They are as follows:
1.InputStream classes
2.OutputStream classes
1.InputStream:
- This abstract class serves as the base class for all byte input stream classes.
- It provides methods like read() and read(byte[] buffer) to read bytes from a source.
2.OutputStream:
- This abstract class is the base class for all byte output stream classes.
- It provides methods like write(int b) and write(byte[] buffer) to write bytes to a destination.
-Examples of byte stream classes:
FileInputStream: Reads data from a file as a sequence of bytes.
FileOutputStream: Writes data to a file as a sequence of bytes.
ByteArrayInputStream: Reads data from an in-memory byte array.
ByteArrayOutputStream: Writes data to an in-memory byte array.
2.Character Stream Class
- Character streams in Java are designed for handling the input and output of characters. They use 16-bit Unicode characters.
- character stream classes are mainly used to read characters from the source and write them to the destination.
- Character streams are more efficient than byte streams. They are mainly used for reading or writing to character or text-based I/O such as text files, text documents, XML, and HTML files.
( Note: Unicode is a 2-byte, 16-bit character set having 65,536 (i.e. 2^16) different possible characters. Only about 40,000 characters are used in practice, the rest are reserved for future purposes. )
Types of CharacterStream class.
Character stream classes also contain two kinds of classes. They are as follow:
1. Reader Stream classes
2. Writer Stream classes
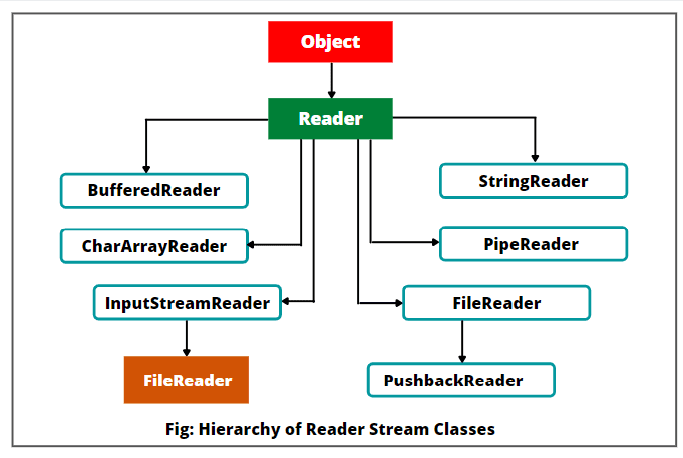
1.Reader Stream:
- The abstract base class for all character input stream classes.
- It provides methods like read() and read(char[] buffer) to read characters from a source.
- It is Similar like Input Stream class The only difference is that Input Stream uses bytes, whereas Reader Stream classes use characters.
2.Writer Stream:
- The abstract base class for all character output stream classes.
- It provides methods like write(int c) and write(char[] buffer) to write characters to a destination.
- Writer stream classes are similar to output stream classes with only one difference that output stream classes use bytes to write while writer stream classes use characters to write.
- In fact, both output stream and writer stream classes use the same methods.
Examples of character stream classes:
FileReader: Reads data from a file as a sequence of characters.
FileWriter: Writes data to a file as a sequence of characters.
StringReader: Reads data from a String object.
StringWriter: Writes data to a String object.
BufferedReader: read characters from the buffered input character stream.
InputStreamReader: This class is used to translate (or convert) bytes to characters.
PipeReader: read characters from the connected piped output.
PushBackReader: This class allows one or more characters to be returned to the input stream.


Comments
Post a Comment